Tephra - solid and molten rock blasted into air
Lava Bombs
Ash
Fumeroles/ poisonous gas - sulphur dioxide
Landslides
Monday, 29 August 2011
Types of Lava
A'a:
Very vicious - flows short distances
slow flowing high basaltic content
cools to a rough surface thats hard to walk on as its sharp and spiky
PaHoeHoe:
Thinner less vicious fast flowing
congeals to form thin crust thats smooth
erupts 1200 - 1200'c
Pillow Lava:
Formed in underwater volcanic eruptions cools to form hard shell
Breaks off tof orm pillow shaped blocks
- Shape of volcano depends on type of lava
- Lava type depends on its mineral content especially the silica content
Very vicious - flows short distances
slow flowing high basaltic content
cools to a rough surface thats hard to walk on as its sharp and spiky
PaHoeHoe:
Thinner less vicious fast flowing
congeals to form thin crust thats smooth
erupts 1200 - 1200'c
Pillow Lava:
Formed in underwater volcanic eruptions cools to form hard shell
Breaks off tof orm pillow shaped blocks
- Shape of volcano depends on type of lava
- Lava type depends on its mineral content especially the silica content
Saturday, 27 August 2011
Different plates
Destructive:
80% of all volcanic activity happens on destructive margins.
Fold mountains:
Constructive: - volcanoes + earthquake
Oceanic crust moves together which makes sea floor spread/ ridges: mid Atlantic ridge: which makes Europe and America to move away from each other
Continental collision: - volcanoes + earthquake
is a phenomenon of the plate tectonics of Earth that occurs at convergent boundaries. Continental collision is a variation on the fundamental process of sub duction, whereby the sub duction zone is destroyed, mountains produced, and two continents sutured together.
E.g.: Andes, Himalayas
Transform/ conservative:
Fault line
Move same direction, at different speeds
Or in alternate directions
80% of all volcanic activity happens on destructive margins.
Fold mountains:
Constructive: - volcanoes + earthquake
Oceanic crust moves together which makes sea floor spread/ ridges: mid Atlantic ridge: which makes Europe and America to move away from each other
Continental collision: - volcanoes + earthquake
is a phenomenon of the plate tectonics of Earth that occurs at convergent boundaries. Continental collision is a variation on the fundamental process of sub duction, whereby the sub duction zone is destroyed, mountains produced, and two continents sutured together.
E.g.: Andes, Himalayas
Transform/ conservative:
Fault line
Move same direction, at different speeds
Or in alternate directions
Thursday, 25 August 2011
Different type of volcano's
Dome Volcano:
In volcanology, a lava dome is a roughly circular mound-shaped protrusion resulting from the slow extrusion of viscous lava from a volcano. The geochemistry of lava domes can vary from basalt to rhyolite although most preserved domes tend to have high silica content.
Lava domes are dynamic structures that evolve over time undergoing various processes such as growth, collapse, solidification and erosion.
Shield Volcano:
A shield volcano is a type of volcano usually built almost entirely of fluid lava flows. They are named for their large size and low profile, resembling a warrior's shield. This is caused by the highly fluid lava they erupt, which travels farther than lava erupted from more explosive volcanoes. This results in the steady accumulation of broad sheets of lava, building up the shield volcano's distinctive form.
Shield volcanoes are built up by effusive eruptions, which flow out in all directions to create a shield like that of a warrior.
Cone Volcano:
A cinder cone or scoria cone is a steep conical hill of volcanic fragments that accumulate around and downwind from a volcanic vent.
Many cinder cones have a bowl-shaped crater at the summit. Lava flows are usually erupted by cinder cones, either through a breach on one side of the crater or from a vent located on a flank.
Cinder cones are commonly found on the flanks of shield volcanoes.
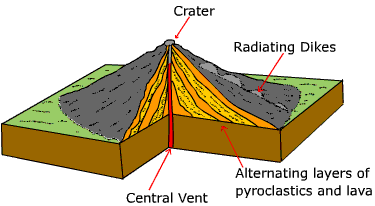
Composite Volcano:
Composite volcanoes, also called strato volcanoes, are formed by alternating layers of lava and rock fragments. This is the reason they are called composite.
Between eruptions they are often so quiet they seem extinct. To witness the start of a great eruption requires luck or very careful surveillance.
Composite volcanoes usually erupt in an explosive way. This is usually caused by viscous magma. When very viscous magma rises to the surface, it usually clogs the craterpipe, and gas in the craterpipe gets locked up. Therefore, the pressure will increase resulting in an explosive eruption.
Monday, 22 August 2011
Plate types
Destructive:
80% of all volcanic activity happens on destructive margins.
Fold mountains:
Constructive: - volcanoes + earthquake
Oceanic crust moves together which makes sea floor spread/ ridges: mid Atlantic ridge: which makes Europe and America to move away from each other
Continental collision: - volcanoes + earthquake
is a phenomenon of the plate tectonics of Earth that occurs at convergent boundaries. Continental collision is a variation on the fundamental process of sub duction, whereby the sub duction zone is destroyed, mountains produced, and two continents sutured together.
E.g.: Andes, Himalayas
Transform/ conservative:
Fault line
Move same direction, at different speeds
Or in alternate directions
80% of all volcanic activity happens on destructive margins.
Fold mountains:
Constructive: - volcanoes + earthquake
Oceanic crust moves together which makes sea floor spread/ ridges: mid Atlantic ridge: which makes Europe and America to move away from each other
Continental collision: - volcanoes + earthquake
is a phenomenon of the plate tectonics of Earth that occurs at convergent boundaries. Continental collision is a variation on the fundamental process of sub duction, whereby the sub duction zone is destroyed, mountains produced, and two continents sutured together.
E.g.: Andes, Himalayas
Transform/ conservative:
Fault line
Move same direction, at different speeds
Or in alternate directions
Thursday, 18 August 2011
Convection Current
Convection is the movement of molecules within fluids (i.e. liquids, gases) and rheids. It cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion can take place in solids.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)